Now Reading: Is the Digital Age Fueling a Brain Rot Epidemic? Understanding the Impact of AI and Social Media
- 01
Is the Digital Age Fueling a Brain Rot Epidemic? Understanding the Impact of AI and Social Media
Is the Digital Age Fueling a Brain Rot Epidemic? Understanding the Impact of AI and Social Media

The term “brain rot,” selected as Oxford’s Word of the Year in 2024, has become a significant concern in the digital era, reflecting widespread fears around a perceived decline in cognitive abilities. As our lives become increasingly intertwined with artificial intelligence and social media, researchers and experts are scrutinizing the potential negative consequences of our reliance on digital technology. But what exactly is brain rot, and why are AI and social media at the heart of this worrying new phenomenon?
Table of Contents
What Is Brain Rot?
“Brain rot” refers to a gradual decline in cognitive functions such as memory, focus, and critical thinking, attributed to overexposure to online content and digital tools. Unlike mere nostalgia for pre-digital times, this is an area of serious scientific inquiry. Studies show that our brains, when constantly subjected to fragmented digital stimulation, may lose their ability to engage deeply with information.
AI Tools: Cognitive Offloading and Atrophy
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized information access and productivity, but this convenience carries cognitive risks. Many users now rely on chatbots and AI-powered search to do their thinking for them, a process called “cognitive offloading.” A 2025 MIT Media Lab study revealed that individuals using AI chatbots for tasks like essay writing experienced less brain engagement and weaker recall compared to traditional searchers or those relying on their own memory.
This dependence on AI has even led researchers to define “AI-Chatbot Induced Cognitive Atrophy” (AICICA). Symptoms reportedly include forgetfulness, reduced focus, and diminished independent thinking, echoing early signs of dementia, especially in heavy AI users. Notably, even large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT risk a kind of “cognitive decline” if trained excessively on low-quality digital content.
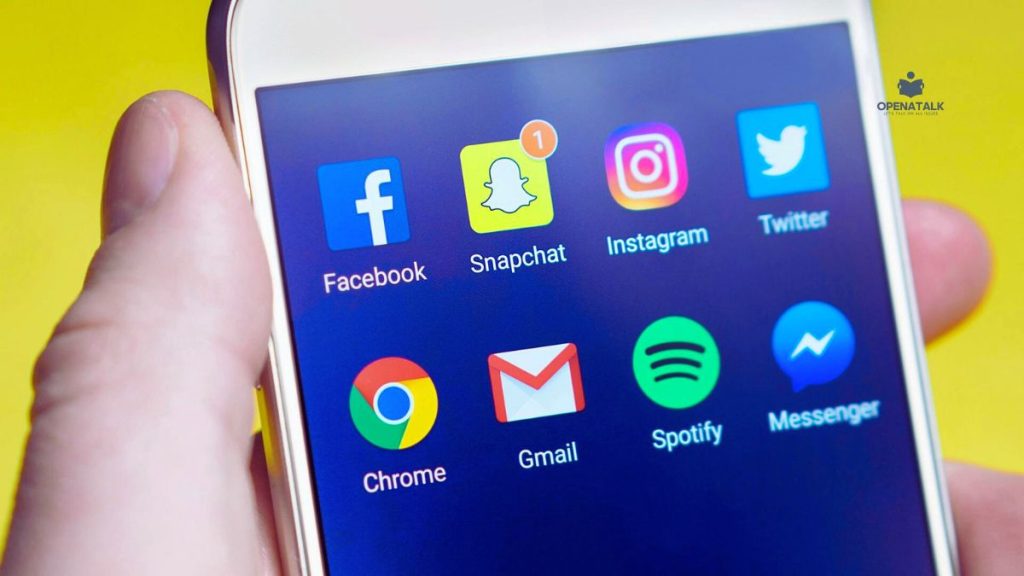
Social Media and the Attention Crisis
Social media, particularly platforms dominated by short-form video such as TikTok, is another culprit in the brain rot epidemic. Infinite scrolling and rapid-fire content overstimulate users’ attention systems, making it harder to concentrate on complex or lengthy tasks. Studies show that this constant need for novel stimulation impairs the brain’s executive functions and memory, and even causes visible structural changes, reducing grey matter in key cognitive areas.
Moreover, social media exploits the dopamine reward system, conditioning users to seek ever more instant gratification and making it more challenging to find satisfaction in slower, more thoughtful pursuits.
Industry Impact and Market Dynamics
Mounting evidence of brain rot has started to impact the technology sector. Giants like Alphabet (Google) and Meta (Facebook, Instagram) face increasing scrutiny, with possible regulatory and design changes on the horizon. Startups focused on mindful tech and digital well-being have an opportunity to lead by building products that enhance, rather than erode, our cognitive resilience.
Societal Implications: Beyond the Individual
The consequences of brain rot are not just personal—they extend to education, civic discourse, and innovation at a societal level. Populations with declining attention spans and critical thinking skills may struggle with complex problem-solving, be more vulnerable to misinformation, and face challenges in the workforce. Recent research ties heavy digital media use to neurobiological changes impacting attention, memory, and impulse control.
Steps Toward Cognitive Resilience
Experts predict that digital well-being, ethical AI design, and enhanced digital literacy will become central focuses in the coming years. There’s a growing call for tech companies to develop tools that prioritize user control and healthy engagement. Education systems may soon integrate “AI literacy” to help future generations critically assess digital content and safeguard themselves against brain rot.
Conclusion: Reclaiming Cognitive Health in the Digital World
The concept of brain rot serves as a powerful warning about the direction in which technology is taking human cognition. Tackling this issue will require collective action from individuals, researchers, policymakers, and the tech industry to ensure AI and social media enhance rather than undermine our brains. As research and debate intensify, the future will likely reward technologies that foster true cognitive growth, resilience, and well-being.



















































Leroy
This piece of writing gives clear idea in support of the new
visitors of blogging, that truly how to do running a blog.
vorbelutr ioperbir
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!